Physics of the cytoskeleton






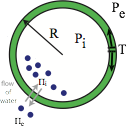
The actin cortex underlies the cell membrane and, through active forces generated by myosins, can deform, flow or change cell shape. Using a combination of hydrodynamic theories of active gels and descriptions of microscopic processes, we aim at understanding the structure of the actin cortex and its role in cytokinesis, bleb formation and cell polarization.
This work involves close collaborations with the experimental groups of Ewa Paluch and Stephan Grill at the Max Planck Institute for Cell Biology and Genetics in Dresden.